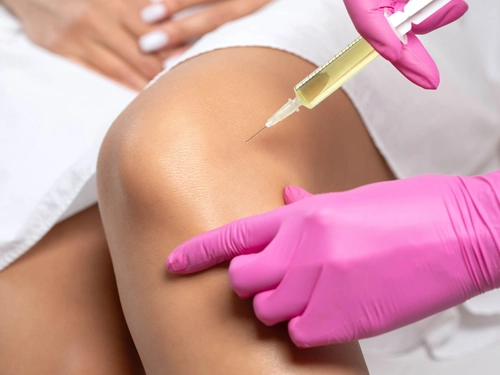
For a number of medical conditions, including knee issues like osteoarthritis, cartilage damage, and ligament injuries, stem cell therapy has emerged as a ground-breaking treatment option.
For those looking for alternatives to conventional surgical interventions, this ground-breaking regenerative therapy has a lot of promise. The idea of stem cell therapy for knees, its procedure, advantages, risks, and success rates will all be thoroughly discussed in this article.
By giving thorough information, we hope to inform and interest prospective patients, fostering confidence in your knowledge and raising the possibility of converting website visitors into patients.
Stem cells are special cells that have the amazing capacity to differentiate into different cell types, regenerate damaged tissues, and differentiate into other cell types. They can be found in the bone marrow, fat, and umbilical cord blood, among other places in the body. To reduce the risk of rejection and ethical concerns, the majority of the stem cells used in knee therapies come from the patient's own body (autologous).
Initial Consultation: A qualified healthcare professional with expertise in regenerative medicine will be consulted at the outset of the process. To determine if you are a good candidate for stem cell therapy for knees, the doctor will review your diagnostic imaging, assess your physical condition, and go over your medical history.
Stem cell harvesting: If a patient is found to be a candidate for treatment, this is the next step. Adipose tissue is the two most frequent source. While adipose tissue extraction is carried out using a minimally invasive liposuction technique, bone marrow aspiration entails extracting stem cells from the hip bone while under local anesthesia.
Stem Cell Processing: Following harvest, the stem cells are isolated and concentrated in a specialized lab. In order to guarantee a high cell count and ideal cell viability, advanced techniques are used.
Injection into the Knee: The concentrated stem cells are then injected directly into the injured knee joint under ultrasound or fluoroscopic guidance as the last step. The cells can target the damaged area and promote tissue regeneration thanks to this precise delivery.
Stem cell therapy for knees offers a ground-breaking strategy for joint repair and pain relief. This minimally invasive procedure seeks to repair damaged tissues, enhance joint functionality, and treat chronic knee conditions by utilizing stem cells' capacity for regeneration. Although the therapy has a lot of potential, it is crucial to speak with a licensed healthcare provider to see if you are a good candidate. Your website can effectively educate and engage potential patients by detailing the procedure, advantages, risks, and success rates. This builds trust in your knowledge and increases the possibility that visitors will become patients.
Living with arthritis can be difficult because it frequently results in chronic joint pain, stiffness, and restricted mobility. For some people, conventional treatments like medicine, physical therapy, and surgery may not be enough to relieve their symptoms. But new avenues for treating arthritis have emerged thanks to developments in regenerative medicine. Modern stem cell therapyfor arthritis offers a promising way to treat arthritis symptoms, encourage tissue repair, and enhance overall joint function. We will examine the fundamentals of stem cell treatment for arthritis, its potential advantages, the course of stem cell therapyfor arthritis, and the current state of research and clinical applications in this comprehensive guide.
It is essential to comprehend the nature of stem cells in order to appreciate the efficacy of stem cell therapy for arthritis. The body contains special cells called stem cells that have the amazing capacity to self-renew and differentiate into various cell types. They may come from adult tissues, umbilical cord blood, or embryonic tissue, among other sources. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) or induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs),which have the capacity to differentiate into bone, cartilage, and other connective tissues, are the most common types of stem cells used in the treatment of arthritis.
In order to promote tissue regeneration and address the underlying causes of joint deterioration, arthritis stem cell therapy targets these issues. The transplanted stem cells work through a number of different mechanisms after being injected into the injured joint:
Stem cell therapy has demonstrated promise in the management of a number of conditions associated with arthritis, including:
The most prevalent type of arthritis, osteoarthritis is characterized by the destruction of joint cartilage and subsequent pain and stiffness in the joints.
The following crucial steps are involved in arthritis stem cell therapy:
Patient Evaluation: Before beginning stem cell therapy, the patient undergoes a comprehensive evaluation that includes a thorough medical history, physical exam, and diagnostic imaging. This evaluation aids in determining the severity of the condition, the suitability of stem cell therapy, and the anticipated advantages.
Stem cell harvesting: Stem cells can be obtained either autologously (from the patient's own body) or allogeneically (from outside sources). The most common sources of autologous stem cells are bone marrow and adipose tissue. The procedure for harvesting stem cells is determined by a number of variables, including the patient's health, the quantity and quality of stem cells needed, and the level of expertise of the healthcare provider.
Processing of stem cells: Following harvest, the stem cells go through isolation and processing in a lab environment. In this step, the desired stem cell population is separated and made transplant-ready. The stem cells' viability and functionality are ensured while the processing methods concentrate and purify them.
Stem Cell Transplantation: Using exact and guided techniques, the prepared stem cells are then injected into the injured joint. Direct injection into the joint space or other therapeutic strategies, like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) or growth factors, can be used to achieve this in order to boost the regenerative response.
Rehabilitation following treatment: A thorough rehabilitation program is typically advised after stem cell therapy. To maximize the effects of the treatment, physical therapy, exercises, and lifestyle changes may be advised. Joint strength, range of motion, and overall functional abilities are all improved by rehabilitation.
There are several potential advantages to using stem cell therapy for arthritis:
Pain relief: Following stem cell therapy, many people report less joint pain. This may result in a higher quality of life and more engagement in regular activities.
Improved Joint Function: Stem cell therapy aims to improve the mobility and function of joints. People may experience improvements in joint stability, range of motion, and flexibility.
Delayed Disease Progression: Stem cells have the ability to slow or stop arthritis from progressing. Stem cell therapy may aid in maintaining joint integrity and halting further deterioration by encouraging tissue repair and regulating the immune response.
Reduced Dependence on Medications: Positive outcomes from stem cell therapy may result in a reduction in the need for painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, potentially reducing the side effects they are associated with.
It's significant to remember that individual results and advantages may differ. The individual variations in outcomes are influenced by a number of variables, including the severity of the arthritis, the patient's general health, and how they responded to treatment.
Stem cell therapy research for arthritis is ongoing, with a focus on better understanding its mechanisms of action, enhancing treatment regimens, and broadening its applications. To investigate the long-term efficacy, safety, and potential combination therapies for improved outcomes, clinical trials are being conducted. It is an exciting field with room for more development and improvement in the years to come.
“As a non-surgical, regenerative method of treating arthritis, stem cell therapy shows great promise. This cutting-edge treatment aims to reduce joint pain, encourage tissue repair, and enhance overall joint function by utilizing the potential of stem cells. Stem cell therapy may be important in the management of different forms of arthritis as research and clinical experience advance, giving hope and a better quality of life to people who suffer from joint pain and restricted mobility.”
It is essential to speak with a reputable healthcare professional with regenerative medicine experience if you are thinking about stem cell therapy for arthritis. In order to help you choose the best arthritis treatment option for you, they can evaluate your unique situation, go over the potential advantages and disadvantages, and walk you through the treatment process.
“In order to promote healing, repair damaged tissues, and reduce pain in the knee joint, stem cell therapy for the knees uses the special qualities of stem cells. Undifferentiated cells called stem cells can differentiate into a variety of specialized cell types and repair damaged tissues.”
To reduce the risk of rejection or unfavorable reactions, this particular therapy frequently uses autologous stem cells, which are derived from the patient's own body. Fat tissue is frequent sources of autologous stem cells for knee therapy.
The process typically starts with the removal of stem cells from the patient's body, which are then isolated and concentrated in a specialized lab. The affected knee joint is then treated by a direct injection of the concentrated stem cells, which is guided by imaging methods like fluoroscopy or ultrasound. The stem cells can target the damaged area thanks to the precise delivery, which encourages tissue regeneration and healing.
“Knee conditions like osteoarthritis, cartilage damage, ligament injuries, and other degenerative or inflammatory conditions are the most common ones that stem cell therapy for knees is used to treat. This therapy aims to lessen pain, enhance joint function, and potentially postpone or even prevent the need for surgical interventions by utilizing the regenerative potential of stem cells.”
While stem cell therapy for the knees has a lot of potential, it's crucial to check with a qualified healthcare provider who specializes in regenerative medicine to see if you are an appropriate candidate. It is essential to stay up to date on the most recent advancements in the field because research into the effectiveness and long-term effects of stem cell therapy for knees is ongoing.
Due to their extraordinary capacity to differentiate into specialized cell types and support tissue regeneration, stem cells are essential in knee therapy. Stem cells can aid in the healing of harmed tissues, the reduction of inflammation, and the relief of pain in the context of knee therapy. Here's a breakdown of how stem cells work in knee therapy:
Differentiation into specialized cells: The remarkable ability of stem cells to differentiate into different cell types found in the knee joint, including chondrocytes (cartilage cells),fibroblasts (ligament cells),and synoviocytes (cells that produce lubricating fluid in the joints),is known as cell differentiation. Stem cells have the capacity to differentiate into these specialized cells when injected into the knee joint, aiding in tissue repair and regeneration.
Production of growth factors and cytokines: Growth factors and cytokines are important signaling molecules in the body, and stem cells secrete bioactive molecules such as growth factors and cytokines. These molecules have the capacity to alter the immediate environment and promote healing. They can support the knee joint's tissue repair mechanisms and stimulate cell growth, decrease inflammation, draw in additional healing cells, and reduce cell death.
Immunomodulatory effects: Stem cells have immunomodulatory properties, which allow them to control the immune response in the knee joint. This is especially helpful for diseases like osteoarthritis, where tissue damage and inflammation are caused by abnormal immune responses. Stem cells can aid in immune system control, control over-the-top inflammation, and support a more balanced healing response.
Paracrine effects: Effects of paracrine signaling on stem cells: Paracrine signaling allows stem cells to have therapeutic effects. Through a process known as paracrine signaling, stem cells can act on nearby cells to encourage their growth, survival, and tissue regeneration. The regenerative processes that stem cells promote are greatly aided by this indirect communication between cells.
Anti-inflammatory properties: Stem cells have shown anti-inflammatory effects, which may be helpful in knee conditions like arthritis that are characterized by chronic inflammation. Stem cells can help relieve pain, enhance joint function, and improve the environment for tissue healing by lowering inflammation in the knee joint.
It's significant to note that research into and comprehension of the precise mechanisms by which stem cells function in knee therapy is ongoing. To better understand their mechanisms of action and maximize their therapeutic potential, research is ongoing. In order to give patients the best care possible, healthcare professionals keep up with the most recent scientific developments, which has resulted in the continued evolution of the use of stem cell therapy for knee conditions.
Yes, autologous stem cells, which are frequently used in knee therapy, are cells that come from your own body. One benefit of using autologous stem cells is that there is less chance of rejection or negative reactions.
For knee therapy, the two primary autologous stem cell sources are:
Bone marrow: The soft, spongy tissue found inside the hollow spaces of bones, most commonly the hip bone, can be used to harvest stem cells for knees. A minimally invasive procedure carried out under local anesthesia is bone marrow aspiration. A small amount of bone marrow, which is a rich source of stem cells, is extracted using a needle.
Adipose tissue (fat): Adipose tissue, also referred to as fat, is a typical source of autologous stem cells for knee therapy. A minimally invasive liposuction procedure can be used to extract the abundant stem cells found in adipose tissue. Before being used for therapy, the stem cells for knees from the extracted fat are processed to isolate and concentrate them.
Stem cells for knees derived from bone marrow and adipose tissue have both been widely used in knee therapy and have demonstrated promising outcomes in promoting tissue regeneration and lowering knee pain.
When using stem cells for knees from another person (allogeneic stem cells),there is no longer a chance of rejection or unfavorable immune reactions. As using your own cells circumvents any ethical issues, it also addresses ethical issues with using stem cells from other sources.
It's significant to note that the precise source of autologous stem cells used in knee therapy may change depending on the knowledge of the healthcare provider, the patient's condition, and other elements. The best source of stem cells for your particular situation will be chosen by a qualified healthcare professional with experience in regenerative medicine.
There is a minimally invasive procedure involved in the stem cell collection for knee therapy. Bone marrow aspiration and adipose tissue extraction are the two primary extraction techniques. Let's examine each approach in more detail:
Extraction of adipose tissue: A second source of stem cells for knee therapy is adipose tissue, also referred to as fat. Using a minimally invasive liposuction technique, stem cells are removed from adipose tissue. Here is a description of the procedure:
Adipose tissue extraction site preparation: The extraction site is cleaned and sterilized. To ensure the patient's comfort throughout the procedure, local anesthesia is used to numb the area.
It's crucial to remember that the precise harvesting technique may change based on the healthcare provider's experience and the unique circumstances of the patient. The best technique for harvesting stem cells for your knee therapy will be decided by a qualified healthcare professional with experience in regenerative medicine.
Before being used for knee therapy, the stem cells are isolated and concentrated in a specialized laboratory procedure after being harvested. Here is a summary of what occurs to the stem cells after they are harvested:
After the required processing and quality control, the stem cells for knees are prepared to be injected into the injured knee joint. The injection is carried out under the supervision of imaging methods like fluoroscopy or ultrasound to guarantee accurate delivery of the stem cells to the desired area.
It's important to remember that the specific laboratory procedures and methods may change based on the qualifications of the healthcare provider and the accepted protocols. The stem cells for knees used for knee therapy will be of a high caliber and meet the requirements for safe and efficient treatment under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional with expertise in regenerative medicine.
In stem cell therapy, the knee joint is typically treated with stem cells that are administered via injection. The intention is to guarantee that the stem cells are precisely directed to the knee's affected area that needs to be treated. An overview of how stem cells are administered to the knee joint is provided below:
Guidance Imaging: Before administering the injection, the medical professional may use imaging methods like ultrasound or fluoroscopy to help them precisely identify the target area within the knee joint. These imaging methods make it possible to see the knee structures in real time, guaranteeing that the stem cells will be placed precisely.
Normally, the entire procedure is carried out as an outpatient procedure, allowing you to go home the same day. Depending on the particulars, such as the complexity of the case and the quantity of injection sites, the procedure's duration may change.
It's crucial to remember that the precise delivery method may change based on the healthcare provider's experience and the unique treatment plan. The diagnosis, the severity of the knee condition, and the treatment objectives decided upon by your healthcare provider will determine the precise areas targeted for injection and the quantity of stem cells for knees delivered.
Knee stem cell therapy is typically well tolerated, and the procedure itself is created to cause the least amount of discomfort possible for the patient. The following is a breakdown of the pain issues related to stem cell therapy for knees:
Local Anesthesia: A local anesthetic is typically used to numb the area around the knee prior to the stem cell injection. By doing this, the procedure is made as painless as possible. In order to lessen the pain of the injection, local anesthesia numbs the skin and underlying tissues.
Discomfort during Injection: Although local anesthesia helps to lessen pain, some patients may still feel a little uncomfortable or temporarily experience more pain during the actual stem cell injection. Individual pain thresholds and the condition being treated specifically can affect the sensation. However, most patients are able to tolerate the discomfort well and it usually passes quickly.
Post-Procedure Sensations: Following the injection, some patients may feel a slight soreness or aching in the knee joint or around the injection site. This discomfort is typically brief and can be treated as prescribed by your healthcare provider or with over-the-counter pain relievers. It's important to remember that each person will experience post-procedure symptoms differently in terms of their duration and intensity.
Personal Pain Tolerance: Everyone has a different threshold for pain, and each person experiences pain differently. While some patients may only feel a little discomfort or pain, others may feel more sensitivity. Your comfort during the procedure can be improved by being open with your healthcare provider about your pain threshold and any worries you may have.
It's important to keep in mind that different people experience pain differently, and the level of discomfort they feel may vary depending on personal factors and the particulars of their situation. Your healthcare provider will take measures to reduce pain throughout the procedure and will offer advice on how to deal with any discomfort that may arise afterward. If you have any particular worries about pain, talking to your doctor about them beforehand can help address them and give you a better idea of what to anticipate during and after your knee stem cells for knees therapy.
There are a number of potential advantages to knee stem cell therapy for those who have knee conditions. Here are some potential advantages of stem cell therapy for knees, though exact results may vary depending on the severity of the condition and each patient's response.
It's important to remember that everyone responds to stem cell therapy differently in terms of effectiveness and specific benefits. The results can vary depending on the severity of the knee condition, general health, and personal response to therapy. To ascertain the potential advantages and suitability of stem cell therapy for your particular knee condition, you must speak with a qualified healthcare provider who specializes in regenerative medicine.
Although stem cell therapy for knees is typically regarded as safe, it's important to be aware of any potential risks and other factors involved. The following are some dangers and things to think about:
To discuss the potential risks, advantages, and suitability of stem cell therapy for your particular knee condition, it is imperative to have a thorough consultation with a licensed healthcare professional who specializes in regenerative medicine. They can give you individualized information and address any worries you might have, enabling you to choose your course of treatment with confidence.
Individuals who receive stem cell therapy for their knees may experience results sooner or later. While some patients might see improvements within a few weeks, others might need a few months to notice a noticeable difference. It's crucial to remember that stem cell therapy works to promote gradual tissue healing and regeneration. Here are some elements that may affect how quickly results will be available:
It's critical to have reasonable expectations for the timeline of stem cells therapy for knees results. The therapy's main objective is to encourage tissue regeneration and ameliorate the underlying condition, which will result in long-term advantages. Your healthcare provider can monitor progress, modify the treatment plan as needed, and offer guidance throughout the recovery process with regular follow-up visits and communication.
It is advisable to speak with a qualified healthcare provider with experience in regenerative medicine about your unique situation, the anticipated time frame for results, and any other aspects that might affect how quickly you will heal.
Insurance coverage for stem cell therapy for knees can vary depending on the specific insurance company, the type of insurance plan, and the nation or region in which you live as of my knowledge cutoff in September 2021. To find out how much stem cell therapy is covered by your insurance, it's important to contact them directly.
Generally speaking, it's important to keep in mind that insurance coverage for stem stem cell therapy for knees may be restricted or nonexistent for some treatments, especially if they are regarded as experimental or have not yet received regulatory authority approval. Since stem cell therapy is a rapidly developing field, insurance companies may have different coverage guidelines.
When exploring insurance coverage for stem cell therapy, consider the following steps:
It's important to remember that insurance coverage policies can change depending on the specifics of each case. Making educated decisions about the cost of stem cell therapy for the knees will be made easier if you stay up to date on any insurance company updates and talk to your doctor about coverage possibilities.
Yes, there are other options besides stem cell therapy for treating knee conditions. Depending on the specific knee condition, its severity, and personal factors, the best alternative will be determined. Here are a few typical options to take into account:
To find the best alternative treatment options for your unique knee condition, speak with a qualified healthcare professional with a focus on orthopedics or regenerative medicine. They can evaluate your condition, go over the advantages and disadvantages of each option, and work with you to create a customized treatment plan that addresses your needs.
Stem cell therapy for the knees may or may not be appropriate depending on the severity of the condition, the particular knee condition, and the patient's general health. While a qualified healthcare professional with experience in regenerative medicine is the best person to assess eligibility, the following general factors should be taken into account for qualified applicants:
It's crucial to speak with a qualified healthcare provider with experience in orthopedics or regenerative medicine to assess your unique condition and decide if stem cell therapy for your knees is right for you. They will discuss the potential advantages and disadvantages of the therapy while taking into account your medical history, imaging findings, and unique situation.
For knee stem cell therapy, there are typically no specific age restrictions. On an individual basis, the suitability for stem cell therapy is assessed taking into account the patient's overall health, medical history, and the particular knee condition being treated. Considerations for age and stem cell treatment for knees include the following:
Since every case is different, choosing stem cell therapy should be done after consulting with a trained medical professional. To decide if stem cell therapy for knees is appropriate for you, they will assess your unique condition, take into account your age, general health, and personal circumstances.
The specific knee condition being treated, the severity of the condition, the patient's general health, and personal response to the therapy are all variables that can affect the success rate of stem cell therapy for knees. It's important to remember that success rates can differ between various studies and reports, and there might be differences in how success is defined in each case. Consider the following important factors when evaluating the success rate of stem cell treatment for knees:
To discuss the success rates specific to your condition, possible outcomes, and the available evidence, speak with a qualified healthcare professional with experience in orthopedics or regenerative medicine. They can review the most recent research, give you individualized information based on your particular situation, and help you set reasonable expectations for the potential advantages and restrictions of knee stem cell therapy.
The specific knee condition being treated, the severity of the condition, and individual healing responses are some of the variables that can affect how long the effects of stem cell therapy for knees last for a given person. Here are some things to think about even though research on the long-term stability of the effects is ongoing:
Regarding the durability of the effects of stem cell therapy for knees, it's critical to have reasonable expectations. Despite the therapy's goal of long-term benefits, patient responses and disease development can differ. To evaluate the effects' longevity and decide whether additional interventions are required, regular follow-up visits with your doctor, adherence to rehabilitation programs, and ongoing monitoring of the knee condition are crucial.
In order to discuss the specifics of your case, including the anticipated duration of the effects, potential need for repeat treatments, and strategies for maintaining optimal long-term outcomes, speak with a qualified healthcare professional who specializes in orthopedics or regenerative medicine.
Stem cell therapy for the knees may in some cases help prevent or postpone the need for knee surgery. The suitability of stem cell therapy as an alternative to surgery, however, depends on a number of variables, including the particular knee condition, the severity of the condition, and individual circumstances. Here are some important things to think about:
Mild to Moderate Knee Conditions: For people with mild to moderate knee conditions, Stem cell therapy for the knees may be a better option than surgery. Early-stage osteoarthritis, minor cartilage injuries, and specific ligament or tendon injuries are a few examples of these conditions. In such circumstances, stem cell therapy may encourage tissue repair and regeneration, possibly minimizing pain and enhancing knee function.
Patient-Specific Factors: A number of patient-specific factors play a role in the decision to pursue stem cell therapy rather than surgery. The patient's overall health and level of fitness, the existence of additional medical conditions that might affect surgery, the person's preference for non-surgical interventions, and the healthcare provider's agreement that stem cell therapy for the knees is an appropriate treatment option are some examples of these factors.
Advanced Knee Conditions: Stem cell therapy might not be enough to avoid surgery in more severe cases, such as advanced osteoarthritis with severe joint damage or complete ligament tears. To address the structural damage in the joint, these conditions frequently call for surgical interventions, such as ligament reconstruction or knee replacement surgery.
Case-by-Case Analysis: Each situation is evaluated individually in order to determine whether surgery is necessary versus stem cell therapy. To choose the best course of action, a qualified healthcare provider with expertise in orthopedics or regenerative medicine can assess your general health, review diagnostic imaging, and evaluate your specific knee condition.
Understanding the best course of treatment for your particular knee condition requires open and in-depth communication with your healthcare provider. Depending on the severity of your condition, your desired course of treatment, and the available options, including stem cell therapy for knees or surgical intervention, they can offer personalized recommendations.
Following knee stem cell therapy, there are usually some guidelines and safety measures to follow. Here are some typical restrictions and precautions to take into account, though the precise guidelines may vary depending on the healthcare provider and the patient's circumstances:
Following knee stem cell therapy, it is essential to carefully adhere to the guidelines and advice given by your healthcare provider. These limitations and safety measures are intended to speed healing, reduce complications, and promote long-term success. Throughout your recovery, don't be afraid to ask your healthcare provider any questions or express any concerns to get answers and advice.
Yes, as part of a thorough treatment plan, stem cell therapy for knee conditions can be combined with other treatments. Depending on the individual's knee condition, its severity, and the healthcare provider's recommendations, a particular treatment regimen will be recommended. These typical procedures may be used in conjunction with stem cell therapy for knees:
The combination of treatments will be determined by the unique treatment plan your healthcare provider has created for you. They will evaluate your unique knee condition, go over your treatment options, and choose the best mix of therapies to meet your needs. To maximize the results of the combined treatments, it's crucial to be open with your healthcare provider, heed their advice, and actively participate in your treatment plan.
Stem cell therapy for knee conditions is not FDA-approved in the United States as of my knowledge's deadline of September 2021. For the treatment of knee conditions, such as osteoarthritis or other injuries related to the knee, the FDA has not approved any specific stem cell products or therapies. It's crucial to remember that there are FDA-approved clinical trials and ongoing studies examining the security and effectiveness of stem cell treatments for a range of medical conditions, including knee conditions.
In order to address unproven and potentially dangerous stem cell therapies, particularly those marketed as autologous stem cell therapies, the FDA has taken regulatory action. These steps are taken to safeguard patient safety and guarantee that treatments are backed by solid scientific evidence.
It's crucial to speak with a licensed healthcare professional who can advise you on how stem cell therapy for knee conditions should be used. They can assist you in understanding the regulatory environment, debating the available evidence, and selecting the best course of treatment for you. To ensure your safety and wellbeing, stay informed about the most recent updates and laws from reliable sources, such as the FDA.
For knee stem cell therapy, there are typically no strict age restrictions. Various factors, including the particular knee condition, the severity of the condition, and personal health considerations, are taken into account when determining a patient's eligibility for stem cell therapy on a case-by-case basis. Here are some important things to think about:
It's crucial to speak with a medical expert with expertise in orthopedics or regenerative medicine to assess your unique knee condition and determine whether you are a good candidate for stem cell therapy. They will talk about the potential advantages, risks, and restrictions of stem cell therapy for your knees while taking a variety of factors into account to offer personalized recommendations.
Yes, athletes' knee injuries can benefit from stem cell therapy for the knees. Due to the demands of their sport, athletes frequently sustain knee injuries like ligament tears (such as ACL or MCL tears),meniscus tears, or cartilage injuries. For athletes looking to recover from knee injuries and get back to their sport, stem cell therapy may be a good treatment option. Here are some important things to think about:
Athletes should seek advice from medical professionals who are skilled at treating sports-related injuries and knowledgeable about the application of stem cell therapy for the knees. These experts can evaluate the athlete's particular injury, go over available treatments, and decide whether stem cell therapy is appropriate for their knee injury. The treatment program can then be modified to fit the athlete's objectives, timetable, and particular sporting needs.
Following stem cell therapy for the knees, a person's recovery time will vary depending on a number of variables, including the specific knee condition, the degree of the damage or injury, the patient's response to healing, and the treatment regimen. While every situation is different and needs to be assessed by a medical expert, the following are some general things to keep in mind:
Working closely with your healthcare professional is essential, as is adhering to their guidance on when to resume regular activities after stem cell treatment for your knees. They will evaluate your particular situation, follow your development, and offer advice based on your unique set of circumstances. Following the recommended rehab plan and gradually increasing your activity level will aid in your recovery and reduce the chance of reinjury.
Yes, to support the healing process, maximize results, and maintain the long-term health of your knees, lifestyle changes or modifications may be advised following stem cell therapy for the knees. Here are some general lifestyle changes that are frequently encouraged, though specific recommendations may vary depending on the circumstances and knee condition being treated of each individual.
These alterations to one's way of living can aid in the recovery process, enhance knee functionality, and support long-term joint health. However, it's crucial to speak with your doctor to receive personalized advice based on your particular knee condition, general health, and needs. Throughout your recovery process, they can offer direction and support and assist you in making the necessary lifestyle changes.
Yes, osteoarthritis and other chronic knee conditions, as well as chronic knee pain, can be treated with stem cell therapy for knees. Long-term inflammation, joint degeneration, or injury are hallmarks of chronic knee conditions. These conditions may be treated with stem cell therapy because it encourages tissue regeneration and lowers inflammation. Here are some important things to think about:
It's important to remember that while stem cell therapy may have some advantages for treating chronic knee conditions, it may not always be effective or completely eliminate symptoms. Individual results may differ, so it's important to set reasonable goals. Consult with a licensed healthcare provider to go over your particular chronic knee condition, the potential advantages of stem cell therapy, and the best course of action for you.
Several variables, including the particular knee condition being treated, the severity of the condition, personal healing responses, and the recommended treatment plan by your healthcare provider, can affect how many stem cell therapy for kneessessions are necessary for knees. While some people might benefit from just one session, others might need several. Here are some important things to think about:
Treatment Response: Different people may react differently to stem cell therapy. While some people might see a significant improvement in their knee condition after just one session, others might need more than one to see the desired results. A person's progress and the treatment's effectiveness are typically considered when deciding whether to schedule additional sessions.
Condition Severity: The number of sessions needed can vary depending on how bad the knee condition is. A single session may be sufficient to encourage tissue regeneration and symptom relief in cases of mild or early-stage conditions. To get the best results, however, more severe or advanced conditions might need more than one session.
Treatment Plan: Your healthcare provider's recommended treatment plan will determine the necessary number of sessions. To create an individualized treatment plan, they will take into account elements like the precise knee condition, the treatment objectives, and the available evidence. To maximize the advantages of stem cell therapy for the knees, this plan might include a particular number of sessions spaced at regular intervals.
Individual Healing Response: Different people's bodies heal and react to treatment in different ways. Age, general health, and the specific knee condition can all influence the healing process. It will be possible to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and make any necessary modifications to the plan of care with the help of routine follow-up visits with your healthcare provider.
Regarding the treatment plan and the potential need for additional sessions, it's crucial to maintain open and regular communication with your healthcare provider. They will keep track of your development, evaluate the efficacy of the therapy, and decide whether additional sessions are required to produce the best results. Keep in mind that your specific needs and treatment response will determine whether you need more sessions.
Several variables, including the specific technique used, the complexity of the case, and individual circumstances, can affect how long the stem cell therapy procedure for knees takes. Here is a general overview of the procedure timeline, though exact times may vary:
From pre-procedure planning to the injection, the entire stem cell therapy for knees procedure for knees can typically be finished in a single day. It's crucial to remember that the precise timeline can change depending on your unique situation and the procedures your healthcare provider follows.
After the procedure, specific rehabilitation instructions or restrictions on weight-bearing may need to be followed. Your healthcare provider will schedule follow-up appointments to check on your progress and modify the treatment plan if necessary. They will also give you comprehensive post-procedure care instructions, including any restrictions or precautions.
For personalized information about the length of the stem cell therapy procedure for your unique knee condition, speak with a qualified healthcare professional who specializes in orthopedics or regenerative medicine. They have experience and follow specific protocols, so they can give you detailed information.
Knee stem cell therapy is typically regarded as risk-free, with a low potential for complications. However, there may be potential side effects, just like with any medical procedure. The potential risks should be understood and discussed with your healthcare provider. Considerations and potential negative effects of stem cell treatment for the knee are listed below:
Prior to receiving knee stem cell therapy, it's crucial to go over potential risks and side effects with your doctor. They will assess your particular situation, take into account your medical background, and give you personalized information tailored to your situation. Additionally, any particular safety precautions or measures to reduce the procedure's risks will be covered.
Yes, as part of a thorough strategy to maximize results, stem cell therapy for knees can be combined with other regenerative therapies. Different regenerative therapies combined may have synergistic effects and increase the potential benefits. The following regenerative therapies can be used in conjunction with stem cell therapy for knees:
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: A concentrated solution of platelets from the patient's own blood is used in platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy. These platelets have growth factors that can aid in tissue regeneration and healing. By supplying more growth factors and bioactive substances to support tissue repair, combining PRP therapy with stem cell therapy may increase the regenerative potential.
Growth Factors: Stem cell therapy can be combined with growth factors, such as those in PRP or from other sources. These growth factors have the ability to increase tissue regeneration, stimulate cellular activity, and aid in the healing process. Growth factors and stem cells combined may result in a more potent regenerative response.
Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Scaffolds: ECM scaffolds are made of synthetic or natural materials that support structural integrity and promote tissue regrowth. To create a three-dimensional environment that encourages cell attachment, migration, and differentiation, they can be used in conjunction with stem cell therapy. ECM scaffolds can aid in the integration of newly formed tissue and the repair of damaged tissue.
Biomaterials and biologics: Stem cell therapy can be combined with a variety of biomaterials and biologics, such as hydrogels, scaffolds, or products derived from the matrix. These substances can act as a supportive matrix for stem cells, improving their ability to survive and integrate into the injured tissue while also encouraging tissue regeneration.
The particular regimen of regenerative therapies will be determined by the individual's knee condition, treatment objectives, and healthcare provider's recommendations. It's crucial to speak with a qualified healthcare provider with expertise in orthopedics or regenerative medicine to determine the best course of action for your particular situation. To improve your outcomes, they will assess your condition, go over your options, and create a customized treatment plan.
The price of stem cell therapy for knees can differ significantly depending on a number of variables, including the precise treatment protocol, the patient's needs, the patient's location, the clinic or healthcare provider, and the cost. I should point out that since I'm an AI language model, I don't have access to current price data. But I can give you an overview of the elements that may affect how much knee stem cell therapy will cost:
Treatment Approach: The cost may vary depending on the precise treatment plan used. For the collection, processing, and administration of stem cells, various clinics may use different procedures, approaches, and technologies. The complexity of the procedure, the healthcare provider's experience, and the caliber of the facilities may all have an impact on the overall cost.
Source of Stem Cells: The price of stem cells may vary depending on their origin. Allogeneic stem cells, which are obtained from a donor, are more expensive than autologous stem cells, which are typically used and come from the patient's own body (such as bone marrow or adipose tissue).
Treatment Strategy: The price may vary depending on the required number of sessions or treatments. Some people might only need one session, while others might require several sessions spaced over a certain amount of time. The specific knee condition, how severe it is, and the healthcare provider's recommendations will all factor into the treatment strategy.
Clinic or Healthcare Provider: Depending on their level of experience, standing in the community, location, and standard of care they offer, various clinics or healthcare providers may have different pricing structures. To get an idea of the price range in your area, it's important to investigate and contrast various providers.
Additional Costs: Pre-procedure assessments, lab tests, imaging studies, follow-up appointments, rehabilitation programs, medications, and other related services may all come at extra cost when using stem cell therapy for the knees. These prices may change based on patient needs and clinic policies.
To get precise and current information about the price of stem cell therapy for knees, it is advisable to speak with medical professionals or clinics directly. They are able to give you a thorough breakdown of the costs and any potential financing options. It's also crucial to speak with your insurance company to find out if any of the treatment costs may be covered.
Keep in mind that when deciding whether to get stem cell therapy for your knees, price shouldn't be the only consideration. Prioritizing the training and experience of the healthcare provider, the safety and effectiveness of the treatment, and the potential advantages and risks of the procedure are essential.
Depending on the underlying cause of the instability, stem cell therapy may be able to help with knee instability or recurrent dislocations. Here are some important things to think about:
It's important to remember that not every case of knee instability or recurrent dislocations may benefit from stem cell therapy. A trained healthcare professional should be consulted before choosing the best course of treatment, including any potential use of stem cell therapy. They will evaluate your particular condition, take into account elements like the reason for the instability, the seriousness of the condition, and your unique needs, and offer tailored treatment recommendations.
Yes, you may need to adhere to particular pre-treatment restrictions and preparations before receiving stem cell treatment for your knees. Your healthcare provider will typically explain these prerequisites and restrictions to guarantee the procedure's security and efficacy. Here are some general considerations, though specific instructions may change depending on the provider and each patient's unique situation:
Medical Evaluation: You will probably go through a thorough medical exam before starting stem cell therapy. A review of your medical history, a physical exam, and possibly diagnostic tests like imaging studies (X-rays, MRIs, etc.) are all possible components of this process. This assessment assists your healthcare provider in identifying any potential risks or contraindications and determining whether stem cell therapy is appropriate for your particular knee condition.
Medication Review: Be sure to let your doctor know about all the drugs you are taking, including prescription, over-the-counter, and dietary supplements. Before the procedure, some medications may need to be changed or temporarily stopped as they may reduce the effectiveness of stem cell therapy or raise the risk of complications.
Smoking Cessation: If you smoke, it's strongly advised that you give it up before receiving stem cell therapy. Smoking can hinder the healing process and lessen the effectiveness of the medicine. You might get support and resources from your doctor to stop smoking.
Fasting Instructions: Specific fasting instructions may be given by your healthcare provider prior to the procedure. When sedation or anesthesia are used, this is typically necessary to ensure an empty stomach. To reduce the risk of complications, adhere to your healthcare provider's fasting instructions.
Hydration: Staying properly hydrated before the procedure may be advised. Adequate hydration can support the overall success of the therapy and improve stem cell collection during harvesting. Observe any hydration recommendations made by your doctor.
Discontinuation of Blood Thinners: Your doctor may advise you to temporarily stop taking any blood-thinning medications, such as anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs, before the procedure if you take them. This reduces the possibility of excessive bleeding while receiving stem cell therapy.
Post-Procedure Planning: Before the procedure, talk with your healthcare provider about post-procedure planning. If sedation or anesthesia is used during the procedure, this may also include making transportation arrangements as well as scheduling any necessary post-procedure care or follow-up appointments.
It's critical to carefully adhere to the detailed pre-treatment instructions that your healthcare provider has provided. The purpose of these instructions is to maximize the potential advantages of knee stem cell therapy while ensuring the safety and efficacy of the procedure. Contact your healthcare provider for clarification and advice if you have any questions or concerns about the pre-treatment requirements or restrictions.
Yes, knee injuries from sports can be treated with stem cell therapy. Sports-related knee injuries can result in cartilage damage, ligament tears (like ACL or MCL tears),meniscus tears, and other types of knee joint harm. The promotion of tissue regeneration and repair, the reduction of inflammation, and an improvement in general knee function are all potential advantages of stem cell therapy. Consider the following important details:
Athletes who suffer from knee conditions brought on by sports injuries may find stem cell therapy to be a helpful treatment option. It provides the chance for tissue repair, quick healing, and non-surgical options. Consult a licensed healthcare provider to assess your specific sports injury, go over your treatment options, and decide whether stem cell therapy is a good option for your knee problem.
While both stem cell therapy and cortisone injections are available as treatments for knee pain, their underlying mechanisms of action and long-term outcomes vary. The following illustrates how cortisone injections and stem cell therapy compare:
Mechanism of Action: Stem cell therapy involves injecting stem cells into the degenerated or damaged knee tissue in an effort to promote tissue repair and regeneration. The body's innate healing mechanisms can be triggered by stem cells, which have the capacity to differentiate into different cell types. The aim is to promote long-term healing and deal with the underlying cause of the knee pain.
Cortisone Injections: An artificial corticosteroid drug, such as cortisone or a comparable drug, is injected into the knee joint during a cortisone injection. In order to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system, corticosteroids suppress the immune system. By reducing inflammation in the knee joint, cortisone injections primarily aim to temporarily relieve pain.
Treatment Period: Stem cell therapy is frequently viewed as a more extensive form of treatment. The goal of using stem cells is to encourage tissue regeneration and repair, which can take time to take place. The effects of stem cell therapy may appear gradually over the course of weeks or months as the body heals itself.
Cortisone injections typically offer momentary pain relief, frequently lasting a few weeks to several months. Injections of cortisone frequently have immediate effects, reducing inflammation and the resulting knee pain. The advantages are only short-lived, and additional care or management may be necessary for the underlying condition.
Long-Term Effects: Stem Cell Therapy: By addressing the root cause of knee pain and fostering tissue repair, stem cell therapy has the potential to provide long-term benefits. It seeks to aid in the body's normal healing process and may bring about long-lasting enhancements in knee performance and pain relief. However, the long-term effects may change based on a person's unique circumstances and the particular knee condition being treated.
By reducing inflammation, cortisone injections primarily relieve pain for a brief period of time. They don't encourage tissue repair or deal with the root of the knee pain. Repeated cortisone injections over an extended period of time may lose some of their effectiveness and may have unfavorable tissue effects, such as cartilage thinning or weakening of tendons.
Suitability for Different Conditions: Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cell therapy may be effective for a variety of knee conditions, including osteoarthritis, ligament sprains, meniscus tears, and cartilage damage. It may help with knee pain's underlying causes and encourage tissue regeneration.
To find the best course of action for your particular knee pain, it's crucial to speak with a trained healthcare professional. They can assess your condition and recommend the best course of action, which may include stem cell therapy, cortisone injections, or a combination of treatments, depending on the severity, underlying cause, and your personal needs.
Most of the time, yes, the stem cells used in knee therapy come from reliable sources. Autologous (obtained from the patient's own body) and allogeneic (obtained from a donor) stem cells are the two main types of stem cells used in knee therapy. Following is a breakdown of each source and its reliable factors:
Autologous Stem Cells: Autologous stem cells are those that come from the patient's own body; they are frequently taken from adipose (fat) tissue or bone marrow. The risk of immune rejection or the spread of infectious diseases is eliminated when stem cells are taken from the patient. In order to use autologous stem cells in knee therapy, the patient's body must first be harvested, after which the cells must be processed and injected again into the knee joint. Autologous stem cell use is typically regarded as trustworthy and safe.
Allogeneic Stem Cells: Allogeneic stem cells are derived from a donor, typically a reliable tissue bank or a carefully vetted donor. To ensure their efficacy and safety, these cells go through extensive testing. In order to guarantee the highest standards for donor screening, cell processing, and storage, reputable tissue banks adhere to strict regulations and quality control measures. To reduce the risk of immune rejection when using allogeneic stem cells, donor and recipient cells must match as closely as possible. Allogeneic stem cells are safe and trustworthy if they are obtained from a reputable source.
It's essential to collaborate with a reputable medical facility or clinic that follows stringent ethical and legal requirements for stem cell therapy. Respectable providers put the safety of their patients first and adhere to set procedures for the collection, processing, and administration of stem cells. They are certified and accredited appropriately, and they follow regulatory requirements.
Researching and selecting a healthcare provider or clinic with a solid reputation, regenerative medicine expertise, and a history of successful patient outcomes are crucial when thinking about stem cell therapy for knees. It is advisable to inquire about the stem cell's origin, the screening procedure, and the provider's adherence to safety regulations. An ethical healthcare provider will put patient safety first and be open and honest about their processes.
Standards and guidelines for stem cell therapy are also provided by regulatory bodies and medical associations. Ask the healthcare provider or clinic if they follow these rules and if they have the appropriate certifications or accreditations.
Remember that confirming the legitimacy of the source of the stem cells used in knee therapy is essential for ensuring your safety and the efficacy of the treatment. You should also keep lines of communication open with your healthcare provider.
Yes, stem cell therapy may be able to help older adults with knee problems. The likelihood of developing knee conditions like osteoarthritis or degenerative joint diseases rises with age. By encouraging tissue regeneration, lowering inflammation, and enhancing general knee function, stem cell therapy may be beneficial for older adults with knee conditions. Several crucial factors are listed below:
Tissue Regeneration: Stem cells can differentiate into a variety of cell types, including the cartilage, ligaments, and other parts of the knee joint that make up the tissue that is being replaced. The function of the knee may be improved and pain may be decreased by injecting stem cells into the areas of the knee that have been injured or degenerated.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: In older adults with knee conditions, chronic inflammation is frequently a factor. Due to their anti-inflammatory qualities, stem cells can aid in reducing knee joint inflammation. Stem cell therapy has the potential to lessen pain and increase mobility by lowering inflammation.
Joint Function Improvement: The goal of stem cell therapy is to treat the underlying causes of knee conditions and encourage tissue healing. Stem cell therapy has the potential to enhance knee joint function, increase range of motion, and enhance overall quality of life for older adults by enhancing knee joint health and integrity.
Non-Surgical Approach: Stem cell therapy provides an option for older adults who may not be good candidates for invasive surgical procedures because of their age or underlying health conditions. By avoiding the risks and recovery time involved with surgery, it can offer a conservative treatment option.
Individual Assessment: Depending on the specific knee condition, general health status, and individual needs, stem cell therapy may be appropriate for treating knee conditions in older adults. An expert in regenerative medicine or orthopedics can assess the particular case, take these things into account, and decide whether stem cell therapy is an appropriate course of treatment.
It is significant to note that the effectiveness of stem cell therapy in older adults may differ depending on elements like the seriousness of the knee condition, general health, and individual response to the treatment. Furthermore, it's crucial to talk about your treatment options with a licensed healthcare professional and to have reasonable expectations about the potential advantages of stem cell therapy. Depending on the individual's unique knee condition and current state of health, they can offer tailored suggestions and advice.
The type and severity of the knee condition, the patient's general health, and their response to the treatment are some of the variables that can affect the success rate of stem cell therapy for particular knee conditions. It's important to note that as an AI language model, I am unable to provide precise success rates or access to real-time clinical data. Depending on the specifics of each patient's case and the available scientific data, the success rate of stem cell therapy can change. Here are some general ideas to keep in mind:
Osteoarthritis: The treatment of knee osteoarthritis with stem cell therapy has shown promise. Studies have shown improvements in pain relief, improved knee function, and cartilage regeneration in some people, though success rates can vary. The stage and severity of osteoarthritis, as well as the chosen treatment plan, may affect the success rate.
Ligament Injuries: The treatment of ligament injuries, such as tears of the ACL or MCL, may involve the use of stem cell therapy. The extent and location of the injury, the chosen course of treatment, and individual factors can all affect the success rate. While some people might benefit and have improved knee stability, more research is required to determine more exact success rates.
Meniscus Tears: Research suggests that stem cell therapy may help to speed up meniscus healing and lessen the symptoms brought on by meniscus tears. The size and location of the tear, the chosen treatment protocol, and individual factors can all affect the success rate. Although there is mounting evidence in favor of stem cell therapy for meniscus tears, more studies are still required to pinpoint the exact success rates.
Cartilage Damage: Knee cartilage damage may be treated with stem cell therapy, according to research. Success rates can vary depending on the degree and location of cartilage damage, the chosen treatment strategy, and personal factors. Studies have revealed that for some people, pain management, cartilage regeneration, and functional outcomes have improved.
To learn more about the specific success rates of stem cell therapy for your particular knee condition, speak with a qualified healthcare professional with a focus on orthopedics or regenerative medicine. They can assess your case, take into account pertinent considerations, talk about the available scientific evidence, and offer specialized information based on their knowledge and experience. They will be able to give a more precise evaluation of the likelihood of success for your particular knee condition.
Yes, post-operative knee rehabilitation using stem cells is possible. Stem cell therapy can be used as part of the rehabilitation process after having knee surgery, such as ACL reconstruction, meniscus repair, or joint replacement, to enhance healing, promote tissue regeneration, and support overall recovery. Here are some ways that stem cell therapy can help with knee rehabilitation following surgery:
Tissue Healing and Regeneration: Stem cells have the capacity to differentiate into a variety of cell types, including the ligaments, cartilage, and other parts of the knee joint. This process is known as tissue healing and regeneration. Stem cells can be injected into the surgically repaired knee to aid in tissue healing, repair of damaged structures, and tissue regeneration. This might speed up the healing process and improve the surgical intervention's long-term results.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Following knee surgery, inflammation is a common reaction. Stem cells have anti-inflammatory properties that can help lessen pain, swelling, and inflammation after surgery. Stem cell therapy can help in the management of post-operative inflammation by suppressing the immune response and modulating inflammatory processes, enabling a quicker and more comfortable recovery.
Rehabilitation and functional recovery: By encouraging tissue regeneration and healing, stem cell therapy can support the rehabilitation process and boost the efficiency of physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises. Combining stem cell therapy with specific rehabilitation exercises may improve knee mobility and functionality by improving muscle strength, joint stability, and functional recovery.
Reduction of Scar Tissue Formation: Scar tissue can form after knee surgery. Excessive scar tissue can affect the flexibility and performance of joints. Stem cell therapy may lessen the formation of excessive amounts of scar tissue and encourage more orderly tissue healing, improving knee function in general.
It's crucial to remember that the specific application of stem cell therapy for post-operative knee rehabilitation will depend on a number of variables, including the type of surgery performed, the person's unique condition, and the healthcare provider's recommendations. To choose the best course of action for your post-operative knee rehabilitation, speak with a qualified healthcare provider with expertise in orthopedics or regenerative medicine. They can assess your particular situation, take into account the surgical procedure carried out, and create a tailored treatment plan that might include stem cell therapy as part of your thorough rehabilitation program.
Yes, there are some restrictions and contraindications to using stem cells to treat knee problems. Though generally safe and well-tolerated, stem cell therapy may not be appropriate for everyone. The following are some restrictions and indications to be aware of:
Severe Knee Instability: Patients with complete ligament tears or severe knee instability who need immediate surgical intervention may not be candidates for stem cell therapy. Surgery may be the best course of action in such circumstances for repair or reconstruction.
Advanced Osteoarthritis: The effectiveness of stem cell therapy may be constrained in cases of advanced osteoarthritis where there is significant joint degeneration and bone-on-bone contact. In such cases, other forms of treatment, like joint replacement surgery, may be more appropriate.
Active Infection: Stem cell therapy might not be advised if there is an active infection in or around the knee joint until the infection has been effectively treated and cleared up. This is done to stop the infection from spreading or the healing process from being hampered.
Blood or Bleeding Disorders: Some blood or bleeding disorders can make it more likely that a patient will bleed excessively during a stem cell therapy procedure. In these circumstances, it might be necessary to delay the procedure or consider other treatment options.
Pregnancy: Due to potential risks to the growing fetus, stem cell therapy is typically contraindicated during pregnancy. If you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant, it's critical to let your doctor know.
Allergies or Sensitivities: It's important to let your doctor know if you have any known allergies or sensitivities to any of the substances used in stem cell therapy, such as the agents used in harvesting or processing the cells. They will decide if other options or safety measures are necessary.
Certain Medical Conditions: Before receiving stem cell therapy, certain medical conditions or comorbidities may need to be carefully considered and evaluated. Active cancer, autoimmune conditions, uncontrolled diabetes, and immunodeficiency conditions are a few examples. The safety and efficiency of the procedure could be affected by these circumstances.
To assess your unique situation and decide whether stem cell therapy is appropriate for your knee condition, it's imperative to speak with a qualified healthcare professional with experience in orthopedics or regenerative medicine. Before advising the best course of treatment for you, they will consider any restrictions or contraindications, your medical history, and a thorough evaluation.
In the treatment of knee meniscus tears, stem cell therapy has indeed shown promise. A common knee injury that can result in pain, swelling, and restricted motion is a meniscus tear. Here are some important factors to think about, even though the effectiveness of stem cell therapy for meniscus tears is still being investigated and its use may vary depending on individual circumstances:
Tissue Regeneration: Stem cells have the capacity to differentiate into different cell types, including those found in the meniscus, which is useful for tissue regeneration. It's thought that introducing stem cells into the damaged meniscus will encourage tissue regeneration and repair. The intention is to speed up the meniscus's recovery by promoting the body's natural healing process.
Reduction of Symptoms: Meniscus tears treated with stem cell therapy may experience a decrease in symptoms like pain, swelling, and restricted knee movement. Stem cell therapy has the potential to lessen the signs and symptoms of meniscus tears by encouraging tissue healing and lowering inflammation.
Potential for Cartilage Formation: Meniscus tears can occasionally be accompanied by concurrent cartilage damage, which raises the possibility of cartilage formation. The cartilage-forming cells known as chondrocytes can be formed from stem cells. Stem cell therapy therefore has the potential to encourage the growth of new cartilage in the knee joint in addition to meniscus healing.
Individual Evaluation: Depending on the type and location of the meniscus tear, the severity of the injury, and the patient's general health, stem cell therapy may be appropriate for meniscus tears. A medical expert with expertise in orthopedics or regenerative medicine can assess the particular case, take these things into account, and decide whether stem cell therapy is an appropriate course of treatment.
It's important to remember that although some studies have found success with stem cell therapy for meniscus tears, more research is required to determine its best use, long-term effectiveness, and ability to compete with other treatment modalities. Meniscus tears should be treated based on an individual assessment by a trained healthcare professional that takes into account the extent of the tear, any accompanying injuries, and the patient's general health.
To learn more about the potential advantages and disadvantages of stem cell therapy for your particular meniscus tear, speak with a healthcare professional with expertise in orthopedics or regenerative medicine. They can offer you individualized guidance toward the best course of treatment based on your particular circumstances.
Depending on the precise treatment strategy and the laws of the nation or region where the therapy is being administered, the manipulation or modification of stem cells used in knee therapy may vary. Here are some general ideas to keep in mind:
Unmanipulated Stem Cells: In some instances, the patient's own body's (autologous) or a donor's (allogeneic) stem cells are used in knee therapy without any significant manipulation or modification. These pure stem cells may be drawn from adipose or bone marrow tissue, processed, and then prepared for injection into the knee joint. The goal is to make use of the stem cells' inherent qualities and capacity for regeneration without changing them.
Minimal Manipulation: Some stem cell therapies only slightly alter the cells in order to improve their capacity for regeneration. To increase the potency of the stem cells, processes like concentration or purification may be used. However, the manipulation is usually restricted to preserving the fundamental properties of the stem cells and avoiding substantial genetic or structural alterations.
Expanded or Cultured Stem Cells: Before being used for knee therapy, stem cells may occasionally be expanded or cultured in a lab to increase their population. In order to produce a larger population of stem cells for transplantation, this process involves encouraging the cells to divide and multiply. To ensure the safety and effectiveness of the cells, it's crucial to note that the expansion or culture process must be carried out in accordance with applicable laws and quality standards.
Working with a qualified healthcare professional or facility that complies with legal requirements and employs cutting-edge stem cell therapy techniques is essential. Reputable providers place a high priority on patient security and adhere to set procedures for the collection, processing, and use of stem cells. They will ensure that any manipulation or modification of stem cells is carried out within the confines of recognized scientific and ethical standards because they will have the necessary certifications and accreditations.
It's important to discuss the specific procedures and techniques used with your healthcare provider when thinking about stem cell therapy for knees. In order to ensure transparency and assist you in making well-informed decisions about your treatment options, they can provide information about the modification or manipulation of stem cells.
Traditional knee surgery and knee stem cell therapy are two different ways to treat knee conditions. Here is an evaluation of the two:
Invasiveness
Stem cell therapy is frequently regarded as a minimally invasive procedure. It entails the injection of stem cells, either from the patient's own body (autologous) or from a donor (allogeneic),into the injured knee joint. Large incisions or a lot of tissue disruption are not necessary.
Traditional knee surgery is an invasive procedure that typically involves larger incisions and significant tissue disruption, such as knee replacement or ligament reconstruction. It frequently necessitates the use of anesthesia, a stay in the hospital, and a prolonged recovery period.
Healing and Tissue Repair
Stem Cell Therapy: In order to encourage tissue regeneration and repair in the knee joint, stem cell therapy is used. Stem cells have the capacity to differentiate into a variety of cell types, such as the ligaments, cartilage, and other parts of the knee that are found in the knee. Addressing the root cause of the knee condition and promoting the body's self-healing mechanisms are the objectives.
Traditional Knee Surgery: In traditional knee surgery, damaged tissues, such as torn ligaments or severely deteriorated cartilage, are frequently removed or repaired. The objective is to give the knee joint stability and functionality again. It might not, however, actively encourage tissue regeneration or repair.
Recovery Period
Stem cell therapy: Compared to open knee surgery, stem cell therapy typically requires less time to heal. Patients may experience less post-operative pain because it is a minimally invasive procedure, they may spend less time in the hospital (if any),and they can frequently return to their regular activities and rehabilitation sooner.
Traditional Knee Surgery: A longer recovery period is usually required after traditional knee surgery. Depending on the precise procedure done, the degree of recovery can vary, but it may require weeks or months of rehabilitation, physical therapy, and activity restrictions.
Complications and Risks
Stem cell therapy is generally regarded as risk-free and safe, with few side effects. However, there is always a chance of infection, bleeding, allergic reactions, or other uncommon adverse events, just like with any medical procedure. When compared to the risks of conventional knee surgery, stem cell therapy is generally less risky.
Traditional Knee Surgery: Traditional knee surgery comes with the standard surgical risks, such as anesthesia-related issues, bleeding, infection, blood clots, and post-operative discomfort. Additionally, the procedure itself may carry risks, such as implant-related complications in joint replacement surgery.
Suitability for Various Situations
Various knee conditions, such as osteoarthritis, ligament injuries, meniscus tears, and cartilage damage, may be treated with stem cell therapy. It aims to promote tissue regeneration and address the underlying cause of the knee condition.
Traditional Knee Surgery: When non-surgical treatments are ineffective for treating more severe or advanced knee conditions, traditional knee surgery is frequently advised. When all other conservative measures have failed or are inappropriate for the patient's condition, it is usually carried out.
It's crucial to remember that whether stem cell therapy is preferable to traditional knee surgery depends on the precise knee condition, its severity, and individual factors. It is advisable to speak with a qualified healthcare provider with experience in orthopedics or regenerative medicine to assess your unique situation and choose the best course of action for your knee condition. Depending on your particular circumstances, preferences, and treatment objectives, they can offer you individualized guidance.
Stem cell therapy for pediatric knee conditions is a topic that needs careful consideration and is still being researched. While stem cell therapy has promise for treating a range of orthopedic conditions, including knee conditions, research into its application in pediatric populations is still ongoing. The following are some crucial considerations:
Legal and Ethical Issues: The use of stem cell therapy in children raises both legal and ethical issues. Pediatric patients' long-term responses to stem cell therapies are still being thoroughly investigated. The use of stem cell therapy in children may be subject to specific rules and regulations set forth by regulatory bodies.
Safety and Efficacy: It is important to thoroughly assess the safety and effectiveness of stem cell therapy for children's knee conditions. The potential effects of stem cell therapy on the growth and development of pediatric patients must be thoroughly investigated because they present special physiological and developmental considerations. To determine the safety profile, dosage, and long-term effects of stem cell therapy in pediatric knee conditions, more research is required.
Alternative Treatment Options: Unlike adult knee conditions, pediatric knee conditions such as ligament injuries, growth plate fractures, or developmental abnormalities may require a different approach to treatment. Conservative therapies, physical therapy, bracing, and pediatric-specific surgical interventions might be more frequently suggested for these conditions.
Consultation with Pediatric Specialists: If a child has a knee condition, it's crucial to speak with pediatric healthcare professionals who have experience treating pediatric knee conditions, such as pediatric orthopedic surgeons or rheumatologists. They can offer advice regarding viable treatment options, taking into account the particular requirements of the child and the body of available scientific data.
While stem cell therapy has potential for treating knee conditions in both children and adults, treating pediatric knee conditions specifically calls for more research and careful consideration. The most effective and evidence-based treatment options for children with knee conditions should be discussed with healthcare professionals who have a specialty in pediatric orthopedics or regenerative medicine.
Following stem cell treatment for the knees, physical therapy is essential for the recovery process. Physical therapy is crucial for maximizing the effects of the treatment, regaining optimal function, and ensuring a full recovery. Stem cell therapy can promote tissue healing and regeneration. The following are some crucial facets of physical therapy's function:
Optimal Healing and Recovery: Physical therapy encourages proper tissue remodeling, strengthens the muscles surrounding the knee joint, and enhances joint mobility in order to promote optimal healing and recovery. By guiding patients through a personalized rehabilitation program, it seeks to maximize the results of stem cell therapy.
Rehabilitation Exercises: Physical therapists create and recommend particular exercises based on a patient's condition, goals, and response to stem cell therapy. These exercises concentrate on enhancing the knee joint's flexibility, strength, stability, balance, and coordination. Exercises for proprioception, balance, and stretching may all be included.
Functional Improvement: The goal of physical therapy is to improve and restore knee-related functional abilities. Depending on the needs and objectives of the individual, this can include exercises like walking, stair climbing, squatting, jumping, and sports-specific movements. Patients can regain daily function and reach their desired level of function with the aid of functional training.
Gait Training: Physical therapists examine and treat any gait (walking pattern) changes that might have arisen as a result of the knee condition or the stem cell therapy procedure. The main goals of gait training are to correct abnormalities, enhance walking mechanics, and encourage a healthy and effective gait pattern.
Pain management: Manual therapy, modalities (such as heat or cold therapy),and therapeutic exercises are all physical therapy techniques that can help manage pain and discomfort brought on by the condition of the knee or the healing process. Physical therapists can help people gradually increase their activity levels while minimizing pain and can offer advice on pain management techniques.
Education and Home Exercise Program: Physical therapists offer education on proper body mechanics, posture, and movement patterns to help patients prevent re-injury and improve their knee health over the long term. They also create a personalized home exercise regimen for the patient, enabling them to continue their recovery outside of therapy sessions.
The patient, physical therapist, and medical staff all work together during physical therapy. To get the best results from knee stem cell therapy, it's critical to adhere to the physical therapist's advice and instructions, attend scheduled sessions, and actively participate in the rehabilitation program.
Consult a licensed physical therapist with expertise in orthopedic rehabilitation to create a custom treatment plan that takes into account your unique requirements and enhances the effects of stem cell therapy.
Yes, older adults with degenerative knee conditions can benefit from stem cell therapy. The aging population is prone to degenerative knee conditions like osteoarthritis, which can cause pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. By encouraging tissue regeneration, lowering inflammation, and enhancing general knee function, stem cell therapy may be advantageous for older adults with degenerative knee conditions. Here are some crucial things to remember:
Tissue Regeneration: The ability of stem cells to differentiate into different cell types, including those found in cartilage, ligaments, and other parts of the knee joint, is known as tissue regeneration. It is possible to encourage tissue regeneration and repair by injecting stem cells into the degenerated areas of the knee. This could enhance knee function and lessen pain.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Degenerative knee conditions are frequently accompanied by chronic inflammation. Stem cells have anti-inflammatory properties that can aid in reducing knee joint inflammation. Stem cell therapy can lessen inflammation, which helps with pain relief and mobility.
Joint Function Improvement: Joint function is enhanced by stem cell therapy, which aims to treat the underlying causes of degenerative knee conditions and encourage tissue regeneration. Stem cell therapy may enhance joint function, increase range of motion, and enhance overall quality of life for older adults by enhancing the health and integrity of the knee joint.
Non-Surgical Approach: For older adults who may not be good candidates for invasive surgical procedures because of age or underlying health conditions, stem cell therapy offers a non-surgical alternative. It might offer a less invasive treatment option without the risks and recovery time of surgery.
Individual Evaluation: Depending on the specific knee condition, general health status, and individual needs, stem cell therapy may be appropriate for treating degenerative knee conditions in older adults. A medical expert with expertise in orthopedics or regenerative medicine can assess the particular case, take these things into account, and decide whether stem cell therapy is an appropriate course of treatment.
It's critical to remember that the effectiveness of stem cell therapy in older adults may differ depending on a variety of variables, including the severity of the knee condition, general health, and individual response to the treatment. Furthermore, it's crucial to talk with a qualified healthcare professional about your treatment options and to have reasonable expectations about the potential advantages of stem cell therapy. Based on the person's unique knee condition and current state of health, they can offer tailored suggestions and advice.
Stem cell therapy for knee problems in autoimmune disease patients is a complicated subject that needs careful consideration. While stem cell therapy has promise for treating a variety of knee conditions, its use in people with autoimmune diseases needs to be carefully considered, taking into account the nature and severity of the particular autoimmune condition as well as the patient's general health. Here are some important things to think about:
To discuss the potential risks, benefits, and individualized treatment options, it is essential to speak with trained medical experts who have experience treating autoimmune diseases and using regenerative medicine. They can assess the particular autoimmune condition, determine whether stem cell therapy is feasible, and take into account alternative treatment options that might be more appropriate for people with autoimmune diseases.
The effectiveness and safety of stem cell therapy in patients with autoimmune diseases will become better understood as research develops. In order to make well-informed decisions and customize treatment plans based on each patient's particular circumstances and medical requirements, close communication between healthcare professionals and patients is imperative.
Following stem cell therapy for the knees, there may be different limitations on driving or mobility, depending on the precise procedure carried out, the patient's response to treatment, and the advice given by the healthcare provider. Here are some general ideas to keep in mind:
Immediate Post-Procedure Period: It is normal to experience some discomfort, swelling, or restricted mobility in the treated knee immediately following the stem cell therapy procedure. It might not be a good idea to drive in these situations until the symptoms go away and it is safe to do so. It is crucial to abide by the precise instructions your healthcare provider gives you regarding post-procedure restrictions and limitations.
Recovery Period: Depending on the patient and the severity of the knee condition being treated, the recovery period's length can change. Physical therapy, rehabilitation exercises, and rest are frequently advised during this period to aid in the healing process. Following the recommended rehab program is crucial, as is steering clear of any activities that could endanger the knee's recovery or put it under undue strain.
Medication and pain: Medication may be used to treat pain after stem cell therapy, which may impair alertness and concentration. Driving should be avoided while you are still under the influence of painkillers or any other medications that could make it difficult for you to operate a vehicle safely.
Individual Recovery Progress: Everybody's recovery process is unique. It is crucial to pay attention to your body, abide by your doctor's advice, and gradually increase your activity level as tolerated. You'll receive instructions from your doctor on when it's safe to start driving again and to gradually regain mobility.
After receiving stem cell treatment for your knees, it's important to discuss any restrictions or mobility limitations with your healthcare provider. They can make tailored recommendations based on the particulars of your procedure, your progress in recovering specifically, and any additional elements that might affect your capacity to drive safely or take part in particular activities. You can make sure that your recovery is secure and successful by adhering to their advice.
For knee conditions linked to obesity, such as osteoarthritis, stem cell therapy may be taken into consideration as a component of a thorough treatment strategy. While stem cell therapy can aid in tissue regeneration and decrease knee joint inflammation, it's crucial to address the underlying factors, such as obesity, that are causing the knee condition. Here are some important things to think about:
It's crucial to remember that stem cell therapy shouldn't be considered a stand-alone treatment for obesity-related knee conditions. It is a part of a thorough treatment strategy intended to address the condition's multifactorial nature. Individuals can enhance their overall knee health and possibly slow the progression of obesity-related knee conditions by combining stem cell therapy with weight management techniques and lifestyle changes.
There are several options to take into account if the initial stem cell therapy does not produce the desired results. Depending on the particulars of the case, the nature of the knee condition, and the person's reaction to the initial course of treatment, the strategy might change. Here are a few potential outcomes:
Throughout the course of your treatment, it's crucial to keep lines of communication open with your doctor. Based on their clinical expertise and your unique circumstances, they will evaluate your particular case, take into account how well you responded to initial therapy, and recommend the best course of action. Since every case is different, treatment plans will be made specifically to address the needs and objectives of the individual.
Diabetes patients must carefully consider and evaluate the use of stem cell therapy for knee conditions. Diabetes is a chronic disease with impaired glucose metabolism that can affect various organs, including the joints, systemically. Here are some important things to think about:
Healing Impairment: Diabetes can interfere with the body's normal healing processes and slow down tissue regeneration. It can result in decreased blood flow, a weakened immune system, and altered cellular function, all of which could reduce the efficacy of stem cell therapy. It is important to consider how diabetes affects stem cells' capacity for regeneration.
Disease Management: Before considering stem cell therapy, diabetes must be effectively managed. To ensure that blood sugar levels are well-controlled and other aspects of diabetes care, such as medications and lifestyle changes, are optimized, it is crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider who specializes in diabetes management.
Individual Evaluation: Several variables, including the patient's overall health, the severity of their diabetes, and the specific knee condition being treated, will determine whether stem cell therapy is appropriate for treating knee conditions in people with diabetes. The risks and potential benefits must be thoroughly assessed by medical professionals with expertise in diabetes care and regenerative medicine.
Risks and Complications: Diabetes can make any medical procedure, including stem cell therapy, more likely to have complications. This covers dangers like slowed wound healing, infection, and diminished therapeutic response. People with diabetes who are considering stem cell therapy for knee conditions need to carefully consider the risks and complications.
Collaborative Care: When considering stem cell therapy for diabetic patients' knee conditions, a multidisciplinary approach is crucial. To ensure thorough assessment, individualized treatment planning, and ongoing patient monitoring, close cooperation between medical specialists in regenerative medicine, orthopedics, and diabetes management is required.
It's crucial to have a thorough conversation with your doctor about your unique situation, the severity of your diabetes, and the nature of your knee condition. They can offer advice based on your particular situation, assist in balancing the advantages and disadvantages, and choose the best course of action for your knee condition while taking your diabetes management into account.
The source of the stem cells and the particular treatment method are just two of the variables that can increase the risk of stem cell rejection or allergic reactions during knee therapy. Here are some important things to think about:
Autologous stem cells: The risk of rejection or allergic reactions is very low if the stem cells used in knee therapy are taken from the patient's own body (autologous stem cells). This is due to the cells' genetic compatibility and origin from the patient's own tissues, which reduces the risk of immune rejection or allergic reactions.
Allogeneic stem cells: In some circumstances, knee therapy may involve the use of stem cells from a donor (allogeneic stem cells). Despite the generally low risk of allergic or rejection reactions, there is a chance of an immune response because of variations in the tissue type of the donor. However, precautions are taken to reduce the risk, including using immunomodulatory methods to lessen the likelihood of rejection and closely matching the donor.
Processing and Purification: To isolate and concentrate the desired cell population, stem cells used in knee therapy are processed and purified. These procedures are designed to get rid of any potential contaminants or unwanted cells that might cause an allergic reaction or an immune response. The safety and purity of the stem cell product are guaranteed through the application of stringent quality control procedures.
Pre-screening and testing: Patients are typically pre-screened and tested for compatibility and potential negative reactions prior to the administration of stem cell therapy. This could entail reviewing the patient's medical background, running allergy tests, and checking for any infectious diseases. These controls make it possible to choose patients wisely and help identify any potential risks.
Adverse Reactions: Although stem cell therapy is generally regarded as safe, there is a chance for adverse reactions as with any medical procedure. These include localized pain or swelling at the injection site, infection, and bleeding. When using autologous stem cells, severe allergic reactions or immune rejection are uncommon.
Working with a qualified healthcare provider or clinic that adheres to legal requirements, adheres to regulatory requirements, and has experience with stem cell therapy is important. They will evaluate your particular situation, go over potential risks and benefits, and take the appropriate safety measures to reduce the possibility of rejection or allergic reactions.
In order to ensure the safety of the procedure, be sure to tell your healthcare provider about any known allergies, prior adverse reactions to medical treatments, and any other pertinent medical history during your consultation. This will ensure that the necessary steps are taken to reduce any potential risks.
When treating knee conditions in people with a history of cancer, the use of stem cell therapy must be carefully thought out and assessed. The type of cancer, the degree of remission or cure, and the patient's general health status all play a role in the decision to proceed with stem cell therapy in these situations. Here are some important things to think about:
It's crucial to keep in mind that stem cell therapy might not always be advised, especially if there is a higher risk of cancer recurrence or if the risks might outweigh the potential benefits. The individual's general health and wellbeing should always come first in the decision-making process.
It is essential to speak with both your oncologist and a healthcare professional with experience in both regenerative medicine and oncology if you have a history of cancer and are thinking about stem cell therapy for a knee condition. They can offer tailored advice based on your unique situation, taking into account the type of cancer, past medical history, and present state of health.
Stem cell therapy for the knees is being researched further to increase its efficacy in treating a range of knee conditions. The following are some important fields of study and advancement:
Stem cell therapy for knee conditions in people with blood clotting disorders needs to be carefully thought out and assessed. During invasive procedures like stem cell therapy, blood clotting disorders like hemophilia or other coagulation disorders can be risky. Here are some important things to think about:
When using stem cell therapy on patients with blood clotting disorders, it's critical to put safety first and to manage any risks that might be present. It is crucial to seek advice from a medical professional with expertise in hematology and regenerative medicine. They can assess the particular circumstances of the patient, take into account the clotting disorder, and choose the best course of action or other alternatives to address the knee condition while reducing the risk of bleeding.
Hyaluronic acid (HA) injections and stem cell therapy are both options for treating knee conditions, but they have different mechanisms of action and goals. The two methods are contrasted in the following:
Mechanism: By injecting stem cells into the knee's damaged or degenerating areas, stem cell therapy aims to promote tissue regeneration and repair. The stem cells can differentiate into a variety of cell types, including those that make up ligaments, cartilage, and other knee joint components. They also have anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties.
Potential Benefits: Potential advantages include a reduction in knee-related pain, inflammation, and disability thanks to stem cell therapy. In addition to promoting tissue healing and possibly regaining knee function, it aims to address the condition's underlying causes.
Potential Results: Stem cell therapy results can differ from person to person. Significant pain relief, improved joint function, and improved quality of life are possible outcomes for some people. It's crucial to remember that the success of stem cell therapy may depend on a number of variables, including the severity of the knee condition and the patient's reaction to the therapy.
Treatment Method: Autologous stem cells, which are taken from the patient's own body and then injected into the knee joint, are a common component of stem cell therapy. The recovery time varies depending on the patient and the particular treatment plan, and it is frequently carried out as an outpatient procedure.
Mechanism: Hyaluronic acid, a naturally occurring substance found in the synovial fluid of the knee joint, is injected during HA injections. By lessening friction and acting as a lubricant and shock absorber, HA improves joint lubrication and offers momentary relief.
Potential Benefits: In patients with knee osteoarthritis, HA injections are primarily intended to reduce pain and enhance joint function. Particularly for people with mild to moderate knee osteoarthritis, they may help lessen joint inflammation and offer symptomatic relief.
Potential Results: The results of HA injections can be unpredictable. While some people might experience momentary pain relief and increased joint mobility, others might not experience much of a benefit. HA injections typically have short-term effects; subsequent injections may be necessary to maintain the advantages.
Injections of HA are typically given right into the knee joint during treatment. Depending on the patient's response and the particular product used, the quantity of injections and the frequency of treatments may change. The procedure typically takes place in an outpatient setting and doesn't need a long recovery period.
It's crucial to remember that the suitability of stem cell therapy or HA injections depends on a number of variables, including the precise knee condition, disease severity, personal health status, and healthcare provider recommendations. To choose the best course of action for your unique knee condition, you must speak with a qualified healthcare provider with expertise in orthopedics or regenerative medicine. They can offer recommendations and advice that are tailored to your specific situation.
When used for knee conditions in people with weakened immune systems, stem cell therapy must be carefully thought out and assessed. When undergoing any medical procedure, including stem cell therapy, a weakened immune system can present additional risks and considerations. Here are some important things to think about:
Increased Infection Risk: People with weakened immune systems are less able to fend off infections. Infection is a risk associated with stem cell therapy, which involves introducing cells into the body. A compromised immune system may not be able to effectively fight off infection. The immune system is essential for identifying and eliminating potential pathogens.
Immune Response to Transplanted Cells: Immune system-interacting cells are a component of stem cell therapy. Immune reactions or the transplanted cells being rejected may be more likely in people with weakened immune systems. There could be complications if the immune system is unable to control how the body reacts to the transplanted cells.
Management of Underlying Condition: Before considering stem cell therapy, the underlying condition that compromises the immune system must be successfully managed. To make sure that the immune system is as stable and functional as possible, this may entail working with medical professionals with expertise in immunology or the particular condition.
Individual Case Evaluation: Each case must be assessed on an individual basis, taking into account the patient's unique immune system defect, the severity of the disease, and any potential risks related to stem cell therapy. Collaboration between healthcare professionals, including experts in immunology and regenerative medicine, is essential to determine the patient's overall health status, weigh the risks and benefits of various treatment options, and choose the best course of action.
Alternative Treatment Methods: People with weakened immune systems may want to think about alternative methods of treating their knee problems. Physical therapy, pain management techniques, or assistive devices are examples of non-invasive or conservative treatments that may be more effective in managing knee conditions while lowering the risk of immune or infection-related complications.
When administering stem cell therapy to people with weakened immune systems, it's critical to prioritize safety and manage any potential risks. It is crucial to seek advice from a medical professional who has training in both immunology and regenerative medicine. They can assess the individual's unique situation, take into account the condition of the patient's weakened immune system, and choose the best course of action or other options to address the knee condition while lowering immune system risks.
Depending on a number of variables, including the severity of the disease, the underlying knee condition, the patient's response to treatment, and adherence to post-treatment rehabilitation, different people may experience different levels of pain relief and functional improvement after receiving stem cell therapy for the knees. Here are some general ideas to keep in mind:
Pain relief: Stem cell therapy seeks to lessen the discomfort brought on by knee conditions. Others may see more moderate or gradual improvement, while some people may experience significant pain relief. The severity of the knee condition, the person's general health, and their response to the treatment are just a few examples of the variables that may affect how much pain relief is experienced. It's important to have reasonable expectations and realize that complete pain relief might not always be possible.
Functional Improvement: Knee mobility and function are other goals of stem cell therapy. Improvements in range of motion, joint stability, and the freedom to carry out daily activities are possible for people. The degree of functional improvement can vary, and it might take some time for stem cell therapy's regenerative effects to fully take effect. To maximize functional gains, it's crucial to adhere to the suggested physical therapy and rehabilitation protocols.
Individual Reaction: Every patient's reaction to stem cell therapy is different. The way a patient responds to treatment can be affected by things like their age, general health, and the specifics of their knee condition. While some people may see more pronounced pain relief and functional improvements, others might only see modest improvements. To monitor and control expectations throughout the course of treatment, it's crucial to maintain open lines of communication with your healthcare professional.
Rehabilitation and follow-up: Post-treatment rehabilitation is just as important to the success of stem cell therapy as the actual treatment. To maximize the effects of stem cell therapy, physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises are frequently advised. It is essential to carefully adhere to the recommended rehabilitation plan, show up for follow-up appointments, and take part in the healing process.
Long-Term Results: Studies into the durability of pain relief and functional improvement following stem cell therapy are still ongoing. While some people might benefit long-term, others might need more treatments or interventions down the road. Long-term results can also be affected by the person's dedication to leading a healthy lifestyle, which includes proper knee care, exercise, and weight management.
It's crucial to be honest and open with your healthcare provider about the specifics of your knee condition, the expected results, and any potential drawbacks of stem cell therapy. They can offer tailored suggestions and direction based on your particular situation and assist in controlling expectations throughout the course of treatment.
When a person has multiple joints involved in their knee condition, stem cell therapy may be an option. However, a number of factors, such as the precise knee condition, the degree of joint involvement, and the patient's general health, determine whether stem cell therapy is appropriate for such patients. Here are some crucial things to remember:
Evaluation and diagnosis: To ascertain the degree of joint involvement and determine the person's general condition, a thorough examination by a healthcare professional with expertise in orthopedics or regenerative medicine is required. This assessment aids in determining the precise knee condition and whether stem cell therapy is a suitable course of treatment.
Treatment Planning: Individuals with multiple joint involvements may require a treatment strategy that prioritizes the worst-affected joints while also taking into account the overall health of their joints. A combination of stem cell therapy, physical therapy, pain management techniques, and other interventions may be advised depending on the severity and particular requirements of each joint.
Comprehensive Approach: Managing multiple joint involvements frequently calls for a comprehensive strategy that takes into account each affected joint's unique requirements. Depending on the symptoms and condition of each joint, this may involve a combination of non-surgical interventions, like stem cell therapy, and other treatment modalities.
Individualized Treatment: Based on elements like the patient's general health, the severity of the disease, functional restrictions, and treatment objectives, treatment plans for people with multiple joint involvements should be personalized. A personalized strategy makes sure that the treatment is adapted to meet the unique requirements of each joint and maximize results.
Collaboration between Specialists: When treating patients with multiple joint involvements, it is essential that specialists in orthopedics, regenerative medicine, and other pertinent fields work together. This interdisciplinary approach guarantees thorough assessment, treatment planning, and ongoing care to effectively manage the various joint conditions.
To evaluate your unique situation, it's crucial to speak with a qualified healthcare professional with experience in orthopedics or regenerative medicine. They will assess the degree of joint involvement, take into account the overall health of the joints, and decide the best course of action for your various joint conditions, which may include stem cell therapy. By working together, you can make sure that your treatment plan is customized to your specific requirements and maximizes the potential advantages for all affected joints.
It takes time and consideration to find a dependable healthcare provider that provides stem cell therapy for knees. You can use the following steps to aid your search:
Ask for Referrals: Begin by asking for recommendations from reliable people, such as your primary care physician, an orthopedic specialist, or other medical personnel. They might be able to suggest reputable knee stem cell therapy providers.
Research Online: Find healthcare providers or clinics that specialize in regenerative medicine and provide stem cell therapy for knees by conducting an online search. Select service providers with relevant experience and knowledge. To learn more about a company's reputation and level of client satisfaction, read reviews and testimonials from previous clients.
Check Credentials and Certifications: Verify the credentials and certifications of the healthcare providers you are thinking about using. Choose medical professionals who meet the necessary requirements, such as board certification in pertinent specialties and membership in associations for orthopedics or regenerative medicine.
Assess Experience and Expertise: Take into account the clinics' or healthcare providers' experience and knowledge in knee stem cell therapy. Ask about their success rates and patient outcomes, as well as their experience treating knee conditions like yours.
Examine Treatment Protocols and Safety Measures: Enquire about the clinic's or healthcare provider's treatment protocols and safety measures. They should follow moral and legal requirements, evaluate patients thoroughly, collect and process stem cells according to standardized procedures, and put patient safety first at all times.
Consultation and communication: Arrange meetings with prospective medical professionals to go over your knee condition, available options for treatment, and anticipated outcomes. This enables you to evaluate their communication style, openness to responding to your queries, and capacity to offer detailed explanations of the procedure.
Ask About Research and Clinical Trials: Find out if the healthcare provider has taken part in any clinical trials or research involving stem cell therapy for the knees. Actively participating in research shows a provider's dedication to advancing the field and keeping up with the most recent advancements.
Seek Second Opinions: If necessary, think about getting second opinions from several healthcare professionals to get a variety of viewpoints and make sure you are well-informed about your treatment options.
Do not forget that selecting a reputable healthcare provider is crucial to guaranteeing the safety and effectiveness of the treatment. Before making a choice, take the time to do extensive research, ask questions, and weigh various factors. It's also crucial to trust your gut and pick a service provider who makes you feel at ease and confident in their knowledge.
 Advances in Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Hair Loss
Advances in Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Hair LossHair loss is a common problem that affects millions of people worldwide. While there are various treatments available for hair loss, such as medication, hair transplant surgery, and topical treatments, they Read More...
 How Much Do Adipose Derived Stem Cells Cost?
How Much Do Adipose Derived Stem Cells Cost?According to a report by the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery, the cost of stem cell therapy for hair loss can range from $3,000 to $10,000 per session, with multiple sessions required for o Read More...
 Does Stem Cell Therapy Work on Hair Loss?
Does Stem Cell Therapy Work on Hair Loss?Loss of hair is a widespread problem that affects millions of individuals globally. There are numerous therapies available for hair loss, but not all of them may be beneficial for every individual. Read More...